A collaboration between Lewis McLain & AI
Only Two Sovereigns
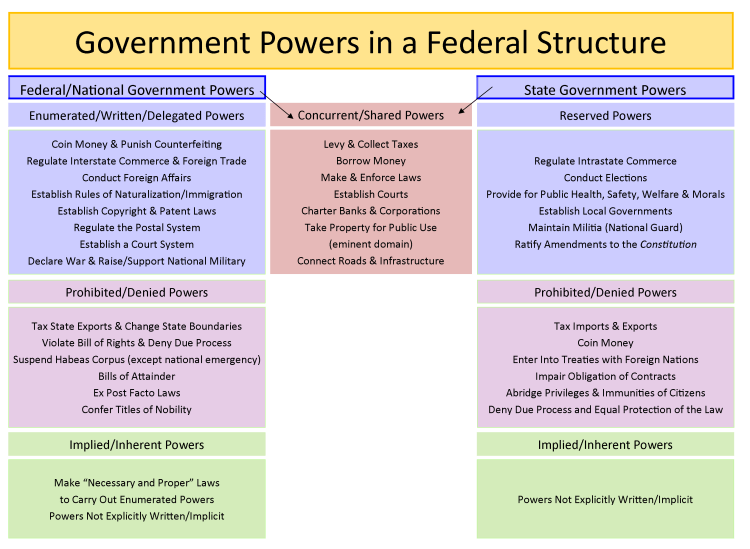
Any serious discussion of Texas local government must begin with a foundational constitutional fact:
In the United States, there are only two levels of sovereign government:
the federal government and the states.
That is the full list.
Counties, cities, school districts, special districts, authorities, councils, boards, and commissions are not sovereign. They possess no inherent authority. They exist only because a state legislature has chosen to delegate specific powers to them, and those powers may be expanded, limited, preempted, reorganized, or withdrawn entirely.
Texas local government is therefore not a story of decentralization.
It is a story of delegated administration, followed—inevitably—by state-directed coordination when delegation produced excessive fragmentation.
The State of Texas as Sovereign and System Designer
The State of Texas is sovereign within its constitutional sphere. That sovereignty includes the authority to:
- Create local governments
- Define and limit their powers
- Redraw or freeze their boundaries
- Preempt their ordinances
- Reorganize or abolish them
Local governments are not junior partners in sovereignty. They are instruments through which the state governs a vast and diverse territory.
From the beginning, Texas made a defining structural choice:
rather than consolidate government as complexity increased, it would delegate narrowly, preserve local identity, and retain sovereignty at the state level. That choice explains the layered system that followed.
Counties: The First Subdivision of State Power
Counties were Texas’s original subdivision of state authority, adopted after independence and statehood from Anglo-American legal traditions.
They were designed for a frontier world:
- Sparse population
- Horseback travel
- Local courts
- Recordkeeping
- Elections
- Law enforcement
During the 19th century, Texas rapidly carved itself into counties so residents could reach a county seat in roughly a day’s travel. By the early 20th century, the county map had largely frozen at 254 counties, a number that remains unchanged today.
Counties are constitutional entities, but they are governed strictly by Dillon’s Rule. They have no inherent powers, no residual authority, and little flexibility to adapt structurally. Once the county map was locked in place, counties became increasingly mismatched to Texas’s urbanizing reality—too small in some areas, too weak in others, and too rigid everywhere.
Rather than consolidate counties, Texas chose to work around them.
Dillon’s Rule: The Legal Engine of Delegation
The doctrine that made this system possible is Dillon’s Rule, named after John Forrest Dillon (1831–1914), Chief Justice of the Iowa Supreme Court and later a professor at Columbia Law School. His 1872 treatise, Commentaries on the Law of Municipal Corporations, emerged during a period of explosive city growth and widespread municipal corruption.
Dillon rejected the notion that local governments possessed inherent authority. He articulated a rule designed to preserve state supremacy:
A local government may exercise only
(1) powers expressly granted by the legislature,
(2) powers necessarily implied from those grants, and
(3) powers essential to its declared purpose—not merely convenient, but indispensable.
Any reasonable doubt is resolved against the local government.
Texas did not merely adopt Dillon’s Rule; it embedded it structurally. Counties, special districts, ISDs, and authorities operate squarely under Dillon’s Rule. Even cities escape it only partially through home-rule charters, and only to the extent the Legislature allows.
Dillon’s Rule explains why Texas governance favors many narrow entities over few powerful ones.
Cities: Delegated Urban Management, Not Local Sovereignty
As towns grew denser, counties proved incapable of providing urban services. The state responded by authorizing cities to manage:
- Police and fire protection
- Streets and utilities
- Zoning and land use
- Local infrastructure
Cities are therefore delegated urban managers, not sovereign governments.
Texas later adopted home-rule charters to give larger cities greater flexibility, but home rule is widely misunderstood. It does not reverse Dillon’s Rule. It merely allows cities to act unless prohibited—while preserving the Legislature’s power to preempt, override, or limit local authority at any time.
Recent state preemption is not a breakdown of the system. It is the system operating as designed.
Independent School Districts: Function Over Geography
Education exposed the limits of place-based governance earlier than any other function.
Counties were too uneven.
Cities were too political.
Education required stability, long planning horizons, and uniform oversight.
Texas responded by removing education from both counties and cities and creating Independent School Districts.
ISDs are:
- Single-purpose governments
- Granted independent taxing authority
- Authorized to issue bonds
- Subject to state curriculum and accountability mandates
ISDs do not answer to cities or counties. They answer directly to the state. This was one of Texas’s earliest and clearest moves toward functional specialization over territorial governance.
Special Districts: Precision Instead of Consolidation
As Texas industrialized and urbanized in the 20th century, the Legislature faced increasingly specific problems:
- Flood control
- Water supply
- Drainage
- Fire protection
- Hospitals
- Ports and navigation
Rather than expand general-purpose governments, Texas created special districts—single-mission entities with narrow authority and dedicated funding streams.
Special districts are not accidental inefficiencies. They reflect a deliberate state preference:
Solve problems with precision, not with consolidation.
The result was effectiveness and speed, at the cost of growing fragmentation.
MUDs and Authorities: Growth and Risk as State Policy
Municipal Utility Districts and authorities are often mistaken for private or quasi-private entities. Legally, they are governments.
MUDs:
- Are created under state law
- Levy taxes
- Issue bonds
- Are governed by elected boards
- Provide essential infrastructure
They allow the state to:
- Enable development before cities arrive
- Finance infrastructure without municipal debt
- Shift costs to future residents
- Avoid restructuring counties
Similarly, transit authorities, toll authorities, housing authorities, and local government corporations exist to isolate risk, bypass constitutional debt limits, and accelerate projects. These are not loopholes. They are state-designed instruments.
The Consequence: Functional Fragmentation
By the mid-20th century, Texas governance had become highly functional—and deeply fragmented:
- Fixed counties
- Expanding cities
- Independent ISDs
- Thousands of special districts
- Authorities operating alongside cities
- Infrastructure crossing every boundary
The system worked locally, but failed regionally.
No entity could plan coherently across jurisdictions. Funding decisions conflicted. Infrastructure systems overlapped. Federal requirements could not be met cleanly. At this point, Texas made another defining choice.
It did not consolidate governments.
It pulled planning and coordination back upward, closer to the state.
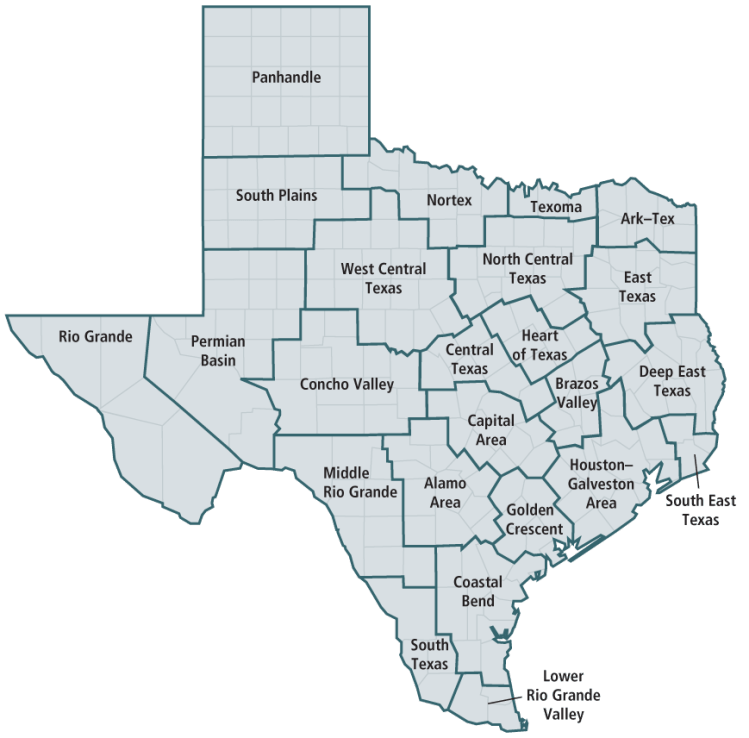
Councils of Governments: State-Authorized Coordination
Beginning in the 1960s, Texas authorized Councils of Governments (COGs) to address fragmentation.
Today:
- 24 COGs cover the entire state
- Each spans multiple counties
- Membership includes cities, counties, ISDs, and districts
COGs:
- Have no taxing authority
- Have no regulatory power
- Have no police power
They exist to coordinate, not to govern—to reconnect what delegation had scattered. Their weakness is intentional. They sit conceptually just beneath the state, not beneath local governments.
MPOs: Transportation Planning Pulled Upward
Transportation forced an even clearer pull-back.
Texas has 25 Metropolitan Planning Organizations, designated by the state to comply with federal law. MPOs plan, prioritize, and allocate federal transportation funding. They do not build roads, levy taxes, or override governments.
MPOs act as planning membranes between federal mandates and Texas’s fragmented local structure.
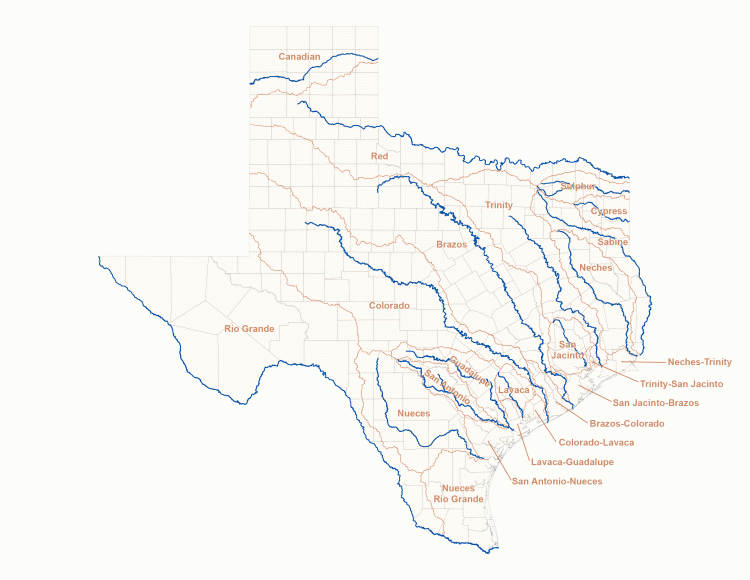
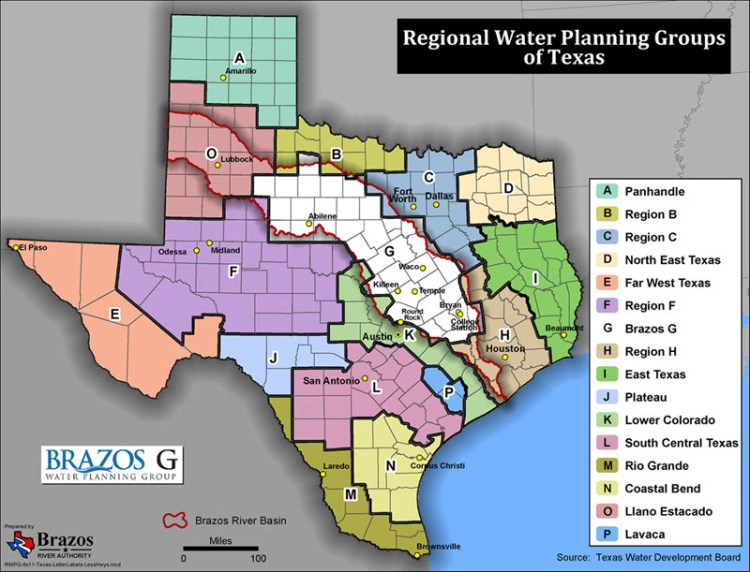
Water: Where Texas Explicitly Rejected Fragmentation
Water planning most clearly demonstrates the limits of local delegation.
Texas spans 15 major river basins, with annual rainfall ranging from under 10 inches in the west to over 50 inches in the east. Water ignores counties, cities, ISDs, and districts entirely.
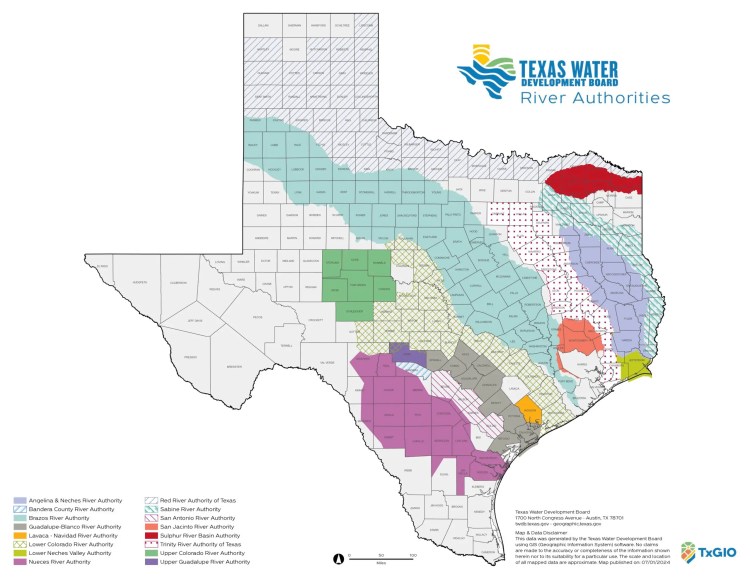
Texas responded by creating:
- Approximately 23 river authorities, organized by watershed
- 16 Regional Water Planning Areas, overseen by the Texas Water Development Board
- A unified State Water Plan, adopted by the Legislature
Regional Water Planning Groups govern planning, not operations. Funding eligibility flows from compliance. This is state-directed regional planning with local execution.
Texas also created 95+ Groundwater Conservation Districts, organized by aquifer rather than politics—another instance of function overriding geography.
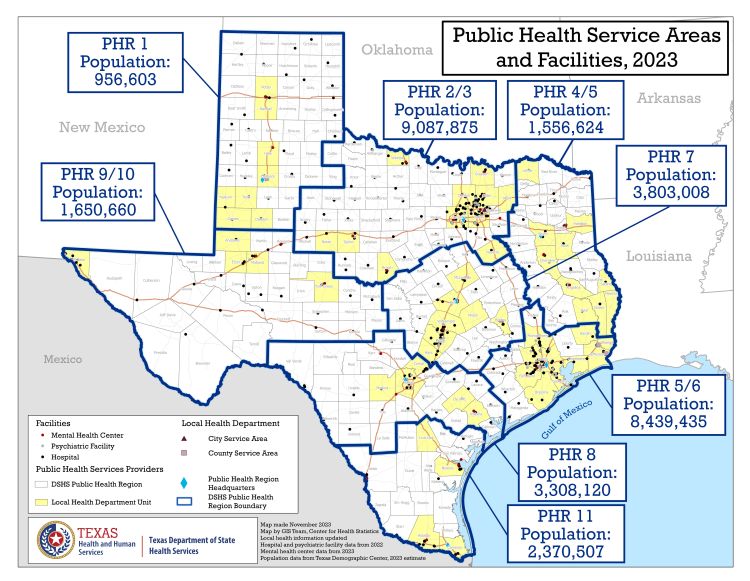
Public Health and Other Quiet Pull-Backs
Public health produced the same result. Disease ignores jurisdictional lines. Texas authorized county, city-county, and multi-county health districts to exercise delegated state police powers regionally.
The same pattern appears elsewhere:
- Emergency management regions
- Workforce development boards
- Judicial administrative regions
- 20 Education Service Centers
- Air-quality nonattainment regions
Each represents the same logic:
- Delegation fragments
- Fragmentation impairs system performance
- The state restores coordination without transferring sovereignty
Final Synthesis
Texas local government did not evolve haphazardly. It followed a consistent philosophy:
- Preserve sovereignty at the state level
- Delegate functions narrowly
- Avoid consolidation
- Specialize relentlessly
- Pull planning back upward when fragmentation becomes unmanageable
What appears complex or chaotic is actually layered intent.
Services are delegated downward.
Planning is pulled back upward.
Sovereignty never moves.
That tension—between delegation and coordination—is not a flaw in Texas government.
It is its defining structural feature.